Overview
Azure Update Manager is a unified, cloud-native service to assess and deploy updates for Windows and Linux servers wherever they run: Azure VMs and Azure Arc-enabled on-premises or multi-cloud machines. It centralizes compliance reporting, lets you patch in real-time or on schedules, and supports maintenance windows, dynamic scoping, pre/post tasks, and granular RBAC.
About WSUS: Microsoft documents that Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) is deprecated and no longer receives new features (it remains supported per lifecycle). The strategic direction is cloud-based management such as Azure Update Manager, Microsoft Intune/Windows Update policies, and Autopatch.
What can you update?
- Windows updates: security, critical, quality updates via Windows Update/Microsoft Update; can also orchestrate when the scan source is WSUS.
- Microsoft product updates: when machines are configured for Microsoft Update (e.g., .NET/SQL components delivered via MU).
- Linux packages: updates from the distro package repositories (apt/yum/dnf/zypper) for common distributions.
- 3rd-party updates: supported when published to Microsoft Update, to WSUS (for environments still using it as scan source), or via Linux repos.
How it works
- Agent interaction: Azure VMs via VM agent; Arc-enabled servers via Arc agent. Update Manager pushes a lightweight extension to assess/apply updates; data resides in Azure Resource Graph.
- Maintenance configurations: Define recurring windows (time zone, duration, recurrence) and patch settings (classifications, reboot behavior, pre/post tasks).
- Assignments: Assign specific machines or use dynamic scope (by subscription, RG, location, tags) to patch at scale.
- Assessments: Enable periodic assessments to refresh compliance automatically every 24 hours.
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription with Microsoft.Maintenance provider registered.
- For non-Azure machines: onboard as Azure Arc-enabled servers (outbound HTTPS 443 required).
- Permissions: Contributor or a custom role that includes Update Manager operations on targeted scopes.
- Supported OS: Windows Server and common Linux distros (see the support matrix).
Configure Azure Update Manager (Portal)
- In the Azure portal, open Update Manager and select
Environment or a specific machine to Assess.
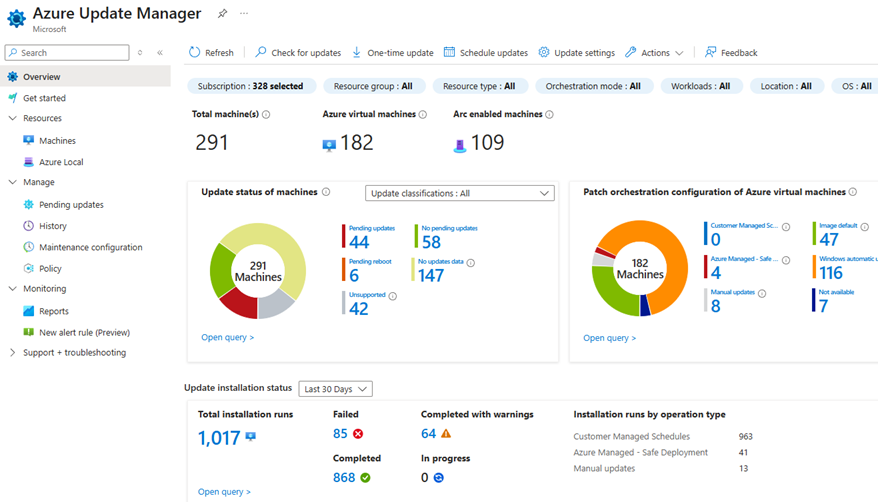 Azure Update Manager
Azure Update Manager - Enable periodic assessment tenant-wide or per scope (recommended) so compliance refreshes every 24 hours.
- Create a Maintenance configuration:
- Set Scope to InGuest Patch.
- Choose Time zone, Start, Duration, Recurrence (e.g., monthly, 2 hours, second Sunday 01:00).
- Patch settings: Windows classifications (Security, Critical), reboot preference; Linux package options.
- Optional: pre/post tasks (scripts/runbooks) to coordinate maintenance.
- Assign scope: target subscriptions/resource groups or dynamic groups (by tags) to include Azure VMs and Arc-enabled servers.
- Use Update now for emergency one-time patching outside schedules.
- Monitor Compliance and Update deployments to track success, reboots, and pending updates.
Configure with Azure CLI (examples)
Below are sample commands to create a maintenance configuration, assign scope, and trigger an on-demand patch. Replace placeholders with your values.
1) Register providers
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.Maintenance
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.HybridCompute2) Create a monthly maintenance window
# Variables
RG=<maintenance-rg>
LOC=<region> # e.g., westeurope
MC=<config-name>
# Create the maintenance configuration (InGuest patching)
az maintenance configuration create \
--resource-group $RG \
--location $LOC \
--name $MC \
--maintenance-scope InGuestPatch \
--maintenance-window-start-date-time "2025-11-09T01:00:00" \
--maintenance-window-duration "02:00" \
--maintenance-window-recur-every "1 Month Second Sunday" \
--time-zone "W. Europe Standard Time"
# (Optional) Enable periodic assessments at scale via policy
# See: https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/update-manager/periodic-assessment-at-scale3) Assign machines to the schedule
# Associate a specific VM
SUB=<subscription-id>
VMRG=<vm-rg>
VMNAME=<vm-name>
MCID="/subscriptions/$SUB/resourcegroups/$RG/providers/Microsoft.Maintenance/maintenanceConfigurations/$MC"
az maintenance assignment create \
--resource-group $VMRG \
--location $LOC \
--resource-type virtualMachines \
--provider-name Microsoft.Compute \
--resource-name $VMNAME \
--configuration-assignment-name $MC \
--maintenance-configuration-id $MCID
# Or assign dynamically by scope/tags in the portal (recommended for scale)4) Patch now (one-time)
# Trigger an on-demand update for a specific VM
# See: https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/update-manager/manage-pre-post-events#manage-the-execution-of-pre-post-event-and-schedule-run
az maintenance applyupdate \
--resource-group $VMRG \
--resource-type virtualMachines \
--provider-name Microsoft.Compute \
--resource-name $VMNAMEConfigure with PowerShell (examples)
Equivalent commands using the Az.Maintenance PowerShell module. Ensure
you're authenticated (Connect-AzAccount) and have the module installed
(Install-Module Az.Maintenance).
1) Register providers
2) Create a monthly maintenance window
Optional Enable periodic assessments at scale via policy See: https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/update-manager/periodic-assessment-at-scale
3) Assign machines to the schedule
Or assign dynamically by scope/tags in the portal (recommended for scale)
4) Patch now (one-time)
Best practices
- Dynamic scope by tags (environment, tier, owner) and time zones for predictable windows.
- Staggered waves: dev/test earlier; prod later with canary groups.
- Reboot planning: align with maintenance windows; consider hotpatch for supported Azure images.
- Compliance: enable periodic assessments and alerts; investigate machines with chronic failures.
- Scan sources: Prefer Microsoft Update for widest catalog; if WSUS remains, ensure it syncs required products/classifications (including 3rd-party if used).
Learn more: About Azure Update Manager · Scheduled patching · Programmatic management · FAQ