Overview
When you onboard servers to Azure Arc, they become first-class Azure resources with rich metadata, tagging, RBAC, and policy. Two core capabilities—Inventory and Change Tracking—provide visibility and auditing across your hybrid fleet without requiring separate CMDB or monitoring infrastructure.
- Inventory: Real-time catalog of installed software, OS details,
extensions, and machine properties via Azure Resource Manager and Azure Resource Graph.
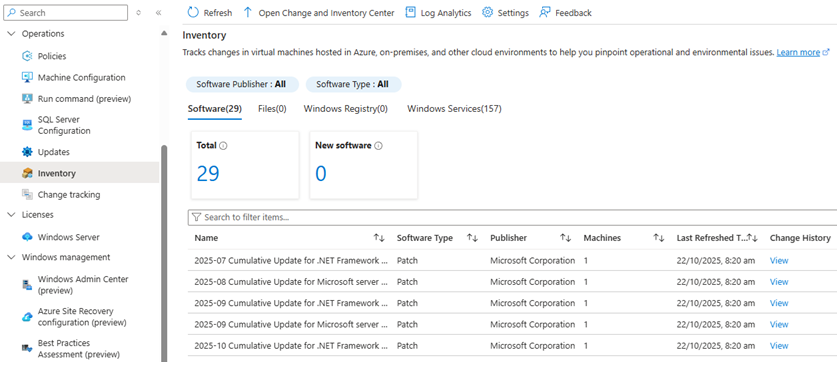 Azure Arc Inventory
Azure Arc Inventory - Change Tracking: Continuous monitoring of file, registry, service,
software, and daemon changes with detailed logs in Log Analytics (ConfigurationChange
and ConfigurationData tables).
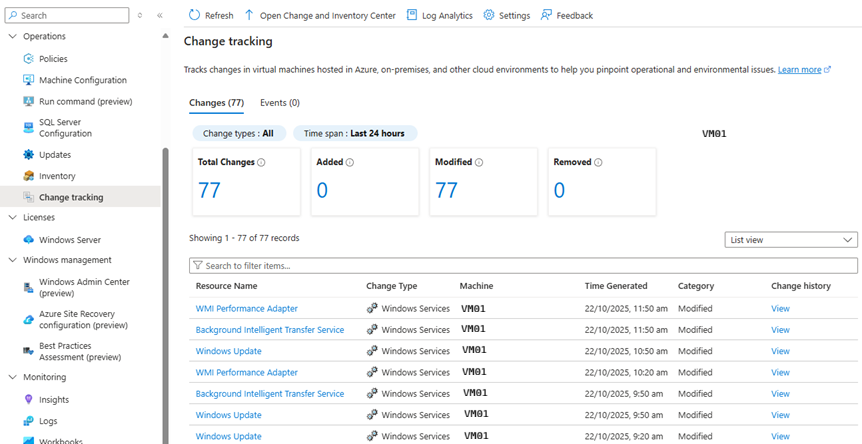 Azure Arc Change Tracking
Azure Arc Change Tracking
Modernization path: If you're migrating from SCCM/ConfigMgr or standalone WSUS/LANDesk, Azure Arc Inventory and Change Tracking deliver cloud-native replacements for inventory, reporting, and change auditing—unified with Azure governance and monitoring.
Benefits
Unified visibility
- Single pane: Query Azure VMs and Arc-enabled on-premises/multi-cloud servers from a single Resource Graph or portal view.
- Azure Resource Manager integration: Arc servers appear as native Azure resources with tags, locks, RBAC, and policy.
- No separate tools: No need for standalone CMDB or inventory databases; all data lives in Azure Resource Graph and Log Analytics.
Continuous change auditing
- Real-time detection: Automated monitoring of software installs/removals, file modifications, registry changes, service state transitions.
- Compliance and forensics: Track "who changed what and when" for security investigations, compliance audits (PCI-DSS, HIPAA, ISO), and troubleshooting.
- Alerting: Set up Log Analytics alerts on critical changes (e.g., Windows service stopped, unauthorized software installed).
Simplified management at scale
- Azure Policy-driven: Deploy Change Tracking at scale via policy; assign data collection rules (DCR) dynamically by tags or scope.
- Cross-platform: Windows Server, Linux (RHEL, Ubuntu, SUSE, Debian, CentOS, Oracle Linux), and hybrid ARM64 machines.
- Flexible queries: Use Kusto Query Language (KQL) in Log Analytics and Azure Resource Graph to build custom reports, dashboards, and automated workflows.
Use cases
1. Asset and software inventory
Scenario: Security and IT ops need a real-time list of installed software, versions, and OS details across thousands of servers in multiple data centers and clouds.
Solution: Azure Resource Graph queries return instant inventories—group by OS, location, tag (environment, application, owner), or installed extensions. Export to Excel, Power BI, or automated compliance reports.
2. Security and compliance auditing
Scenario: Compliance officers must prove that unauthorized software is detected and logged, and that critical services remain running.
Solution: Change Tracking logs all software installs/removals and service state transitions to Log Analytics. Create alerts for high-risk changes (e.g., antivirus service stopped, unapproved software installed). Retention policies keep audit trails for regulatory requirements.
3. Troubleshooting and root cause analysis
Scenario: An application breaks after a weekend deployment; ops need to identify what changed (config file, registry key, service restart).
Solution: Query ConfigurationChange table for the time window and server; drill into file content changes, registry modifications, and software updates. Quickly correlate changes with incidents.
4. Migration and modernization tracking
Scenario: Moving from SCCM to Azure Arc; need to track which servers are onboarded, which extensions are deployed, and which machines still lack monitoring agents.
Solution: Resource Graph shows onboarding status, installed extensions (Azure Monitor Agent, Defender, Update Manager), and missing agents. Tag servers by migration wave and monitor progress with automated queries.
5. Drift detection and configuration management
Scenario: A baseline requires all production servers to have a specific registry key set and a monitoring service running; detect drift automatically.
Solution: Azure Machine Configuration (guest policies) enforces desired state; Change Tracking logs any deviations. Alert on unauthorized config changes and trigger remediation workflows.
Architecture and components
Inventory data sources
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM): Core machine metadata (OS, region, subscription, resource group, tags, provisioning state).
- Azure Resource Graph: Fast, at-scale queries across subscriptions; supports complex filters, joins, and aggregations.
- Arc agent (azcmagent): Heartbeat sync, instance metadata, and extension inventory.
- Machine Configuration agent: Detailed OS and application settings (installed software, services, environment variables).
Change Tracking data flow
- Azure Monitor Agent (AMA): Collects change data from servers and forwards to Log Analytics.
- Change Tracking extension: Windows
(
ChangeTracking-Windows) or Linux (ChangeTracking-Linux); monitors files, registry, services, software, and daemons. - Data Collection Rule (DCR): Defines what to track (paths, registry keys, classifications) and which Log Analytics workspace to send data to.
- Log Analytics tables:
ConfigurationChange: Change events (what changed, when, previous/new values).ConfigurationData: Current inventory snapshot (installed software, services, files).
Tip: Use a single Log Analytics workspace per region or business unit for centralized Change Tracking; assign Arc servers to DCRs by tags (environment, tier, application) for flexible scoping.
Prerequisites
- Azure Arc onboarding: Servers must be Arc-enabled (azcmagent connected).
- Log Analytics workspace: Must be in a supported region for Change Tracking.
- Permissions:
- Inventory: Reader on subscriptions/resource groups to query Resource Graph.
- Change Tracking: Contributor or custom role to deploy DCRs, extensions, and assign monitoring agents.
- Azure Monitor Agent (AMA): Automatically installed when you enable Change Tracking; replaces legacy MMA (Log Analytics agent).
Enable Change Tracking (Portal)
- Navigate to your Arc-enabled server in the Azure portal under Machines - Azure Arc.
- Under Operations, select Change tracking.
- Select Enable using AMA agent (Recommended) and click
Enable.
- This creates a Data Collection Rule (DCR) with a name like
ct-dcr-<guid>. - Installs the Azure Monitor Agent (AMA) and the appropriate Change Tracking
extension (
ChangeTracking-WindowsorChangeTracking-Linux).
- This creates a Data Collection Rule (DCR) with a name like
- Deploy the DCR template (if enabling for multiple machines):
- Download CtDcrCreation.json.
- In the portal, search Deploy a custom template → Build your own template in the editor.
- Load the JSON file, specify the Log Analytics Workspace Resource ID and Resource Group, and deploy.
- Associate machines to the DCR:
- Navigate to Monitor → Data Collection Rules → select your DCR.
- Under Resources, click Add and filter by Machines-Azure Arc or Virtual Machines.
- Select servers and Apply.
- Configure tracking settings (optional):
- In the server's Change tracking page, go to Settings → Data Collection Rule Configuration.
- Add custom Windows Files, Linux Files, or Windows Registry paths to monitor.
- Enable File Content changes (requires linked storage account for snapshots).
- Verify: After 5–10 minutes, query
ConfigurationChangeandConfigurationDatatables in Log Analytics to see change events and inventory snapshots.
Enable Change Tracking (CLI and PowerShell)
Azure CLI
# Variables
RG=<arc-rg>
MACHINE=<arc-machine-name>
LOCATION=<region>
# Install the Change Tracking extension (Windows)
az connectedmachine extension create \
--name ChangeTracking-Windows \
--publisher Microsoft.Azure.ChangeTrackingAndInventory \
--type ChangeTracking-Windows \
--type-handler-version 2.20 \
--machine-name $MACHINE \
--resource-group $RG \
--location $LOCATION \
--enable-auto-upgrade
# Install the Change Tracking extension (Linux)
az connectedmachine extension create \
--name ChangeTracking-Linux \
--publisher Microsoft.Azure.ChangeTrackingAndInventory \
--type ChangeTracking-Linux \
--type-handler-version 2.20 \
--machine-name $MACHINE \
--resource-group $RG \
--location $LOCATION \
--enable-auto-upgrade
# Associate the machine with a DCR (replace with your DCR resource ID)
# This is done via Monitor > Data Collection Rules > Resources in the portal, or via ARM template/policyPowerShell
Query examples (Azure Resource Graph and Log Analytics)
Inventory: All Arc servers by OS and location
// Azure Resource Graph
resources
| where type == 'microsoft.hybridcompute/machines'
| extend OS = properties.osName, OSVersion = properties.osVersion
| project name, OS, OSVersion, location, resourceGroup, tags
| order by name ascInventory: Servers missing Azure Monitor Agent
// Azure Resource Graph
resources
| where type == 'microsoft.hybridcompute/machines'
| where properties.osName == 'windows' or properties.osName == 'linux'
| extend hasAMA = properties.extensions contains 'AzureMonitorWindowsAgent' or properties.extensions contains 'AzureMonitorLinuxAgent'
| where hasAMA == false
| project name, resourceGroup, location, tagsChange Tracking: Software installed in last 7 days
// Log Analytics
ConfigurationChange
| where ConfigChangeType == "Software" and ChangeCategory == "Added"
| where TimeGenerated > ago(7d)
| project TimeGenerated, Computer, SoftwareName, Publisher, ChangeCategory
| order by TimeGenerated descChange Tracking: Windows services stopped
// Log Analytics (Alert candidate)
ConfigurationChange
| where ConfigChangeType == "WindowsServices" and SvcChangeType == "State"
| where SvcPreviousState == "Running" and SvcState == "Stopped"
| where SvcStartupType == "Auto" and TimeGenerated > ago(30m)
| project TimeGenerated, Computer, SvcName, SvcDisplayName, SvcState
| order by TimeGenerated descChange Tracking: File modifications on Linux
// Log Analytics
ConfigurationChange
| where ConfigChangeType == "Files" and Computer contains "linux"
| where TimeGenerated > ago(1d)
| project TimeGenerated, Computer, FieldsChanged, FileSystemPath, FileContentChecksum
| order by TimeGenerated descConfiguration tune-ups and best practices
1. Scope tracking to reduce noise
- Selective paths: Don't monitor entire drives; focus on critical config
directories (
C:\\Program Files\\MyApp\\config,/etc/myapp). - Exclude temp/logs: Avoid tracking
%TEMP%,/tmp, log directories to reduce ingestion volume and cost. - Registry keys: Target specific keys (e.g.,
HKLM\\SOFTWARE\\MyApp) rather than entire hives.
2. Use tags for dynamic scoping
- Tag Arc servers with
environment:prod,tier:web,owner:TeamA. - Assign DCRs by tag filters so new servers automatically inherit Change Tracking without manual enrollment.
- Query Resource Graph by tags to generate environment-specific inventory reports.
3. Set up alerts for critical changes
- Stopped services: Alert when critical auto-start services stop (SQL Server, IIS, monitoring agents).
- Unauthorized software: Alert on software installs where Publisher is not in an approved list.
- Config file changes: Alert when production config files (web.config, httpd.conf) are modified outside change windows.
- Action groups: Route alerts to email, SMS, Logic Apps, or Automation runbooks for automated response.
4. Optimize Log Analytics retention and costs
- Retention: Default 30 days; extend to 90+ days for compliance; archive cold data to Azure Storage for long-term retention at lower cost.
- Data caps: Set daily ingestion caps if Change Tracking volume is unexpectedly high; refine DCR scope to reduce noise.
- Commitment tiers: Use Log Analytics commitment tiers for predictable high-volume workloads (500 GB+/day).
5. Integrate with governance and automation
- Azure Policy: Deploy Change Tracking extensions and DCRs at scale via built-in or custom policies (e.g., "All Arc servers in prod must have Change Tracking enabled").
- Azure Automation runbooks: Trigger remediation workflows when unauthorized changes are detected (revert config, notify owner, open ticket).
- Microsoft Sentinel: Ingest ConfigurationChange events into Sentinel for security analytics, threat hunting, and incident correlation.
6. Monitor Change Tracking health
- Check Heartbeat table in Log Analytics to confirm Arc agents are reporting.
- Query
ConfigurationChange | summarize count() by Computer, bin(TimeGenerated, 1h)to verify continuous data flow. - Review DCR association status in the portal (Monitor → Data Collection Rules → Resources) to ensure servers are attached.
Quick win: Start with a pilot group (e.g., 10 servers in dev) to validate DCR settings, queries, and alerts before rolling out to production at scale. Use Resource Graph to automate bulk server selection by tags.
Migration from legacy solutions
SCCM / Configuration Manager
- Inventory replacement: Azure Resource Graph + Machine Configuration replaces SCCM hardware and software inventory.
- Change auditing: Change Tracking provides equivalent (or better) change detection with cloud-native querying and alerting.
- Compliance baselines: Azure Machine Configuration (guest policies) replaces SCCM configuration baselines and desired state enforcement.
MMA (Log Analytics agent) to AMA
- Azure Monitor Agent (AMA) is the modern replacement for MMA; Change Tracking now uses AMA + extensions.
- Use the migration tool to automate transition: reads MMA-based DCR settings, creates AMA DCR, deploys extensions, removes MMA.
- Compare data across both agents during the migration window to validate parity.